
SpringBoot 结合 Spring Cache 操作 Redis 实现数据缓存
文章目录
!版权声明:本博客内容均为原创,每篇博文作为知识积累,写博不易,转载请注明出处。
系统环境:
- Redis 版本:5.0.7
- SpringBoot 版本:2.2.2.RELEASE
参考地址:
- Redus 官方网址:https://redis.io/
- 博文示例项目 Github 地址:https://github.com/my-dlq/blog-example/tree/master/springboot/springboot-redis-cache-example
一、缓存概念知识
1、是什么缓存
我们日常生活中,经常会接触听到缓存这个词,例如,浏览器清空缓存,处理器缓存大小,磁盘缓存等等。经过分类,可以将缓存分为:
- 硬件缓存: 一般指的是机器上的 CPU、硬盘等等组件的缓存区间,一般是利用的内存作为一块中转区域,都通过内存交互信息,减少系统负载,提供传输效率。
- 客户端缓存: 一般指的是某些应用,例如浏览器、手机App、视频缓冲等等,都是在加载一次数据后将数据临时存储到本地,当再次访问时候先检查本地缓存中是否存在,存在就不必去远程重新拉取,而是直接读取缓存数据,这样来减少远端服务器压力和加快载入速度。
- 服务端缓存: 一般指远端服务器上,考虑到客户端请求量多,某些数据请求量大,这些热点数据经常要到数据库中读取数据,给数据库造成压力,还有就是 IO、网络等原因有一定延迟,响应客户端较慢。所以,在一些不考虑实时性的数据中,经常将这些数据存在内存中(内存速度非常快),当请求时候,能够直接读取内存中的数据及时响应。
2、为什么使用缓存
用缓存,主要有解决 高性能 与 高并发 与 减少数据库压力。缓存本质就是将数据存储在内存中,当数据没有发生本质变化的时候,我们应尽量避免直接连接数据库进行查询,因为并发高时很可能会将数据库压塌,而是应去缓存中读取数据,只有缓存中未查找到时再去数据库中查询,这样就大大降低了数据库的读写次数,增加系统的性能和能提供的并发量。
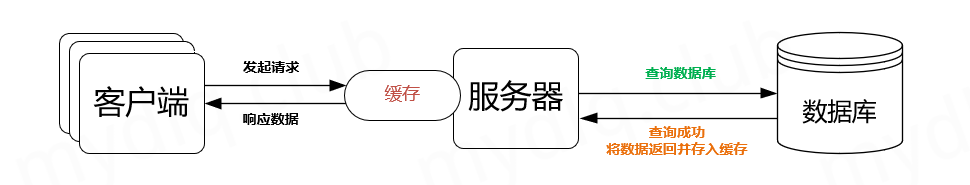
3、缓存的优缺点
优点:
- 加快了响应速度
- 减少了对数据库的读操作,数据库的压力降低。
缺点:
- 内存容量相对硬盘小。
- 缓存中的数据可能与数据库中数据不一致。
- 因为内存断电就清空数据,存放到内存中的数据可能丢失。
二、Redis 概念知识
1、什么是 Redis
Redis 是一个高性能的 Key-Value 数据库,它是完全开源免费的,而且 Redis 是一个 NoSQL 类型数据库,是为了解决 高并发、高扩展,大数据存储 等一系列的问题而产生的数据库解决方案,是一个非关系型的数据库。但是,它也是不能替代关系型数据库,只能作为特定环境下的扩充。
2、为什么使用 Redis 作为缓存
- 支持高可用: Redis 支持 master\slave 主\从机制、sentinal 哨兵模式、cluster 集群模式,这样大大保证了 Redis 运行的稳定和高可用行。
- 支持多种数据结构: Redis 不仅仅支持简单的 Key/Value 类型的数据,同时还提供 list、set、zset、hash 等数据结构的存储。
- 支持数据持久化: 可以将内存中的数据持久化在磁盘中,当宕机或者故障重启时,可以再次加载进如 Redis,从而不会或减少数据的丢失。
- 有很多工具与插件对其支持: Redis 已经在业界广泛使用,已经是成为缓存的首选目标,所以很多语言和工具对其支持,我们只需要简单的操作就可以轻松使用。
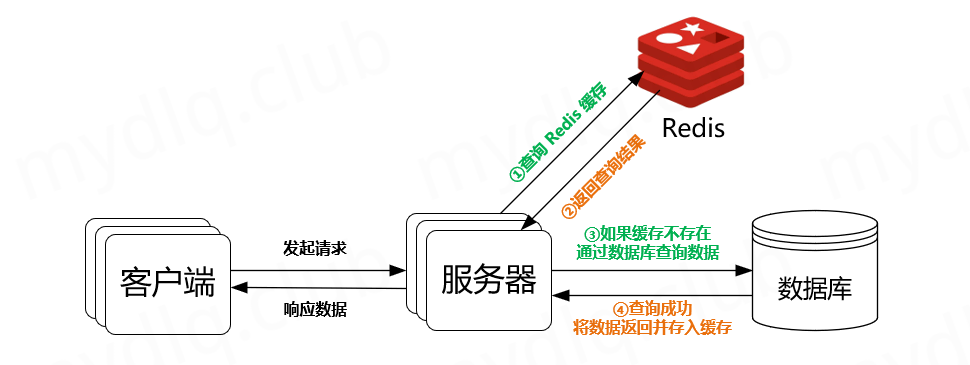
3、Redis 支持的数据类型
Redis 支持的数据结构类型包括:
- 字符串(string)
- 哈希表(hash)
- 列表(list)
- 集合(set)
- 有序集合(zset)
为了保证读取的效率,Redis 把数据对象都存储在内存当中,它可以支持周期性的把更新的数据写入磁盘文件中。而且它还提供了交集和并集,以及一些不同方式排序的操作。
三、缓存后可能遇见的问题
1、缓存穿透

缓存穿透: 指查询一个一定不存在的数据,由于缓存是不命中时需要从数据库查询,查不到数据则不写入缓存,这将导致这个不存在的数据每次请求都要到数据库去查询,造成缓存穿透。
缓存穿透几种解决办法:
- 缓存空值,在从 DB 查询对象为空时,也要将空值存入缓存,具体的值需要使用特殊的标识, 能和真正缓存的数据区分开,另外将其过期时间设为较短时间。
- 使用布隆过滤器,布隆过滤器能判断一个 key 一定不存在(不保证一定存在,因为布隆过滤器结构原因,不能删除,但是旧值可能被新值替换,而将旧值删除后它可能依旧判断其可能存在),在缓存的基础上,构建布隆过滤器数据结构,在布隆过滤器中存储对应的 key,如果存在,则说明 key 对应的值为空。
2、缓存击穿

缓存击穿: 某个 key 非常热点,访问非常频繁,处于集中式高并发访问的情况,当这个 key 在失效的瞬间,大量的请求就击穿了缓存,直接请求数据库,就像是在一道屏障上凿开了一个洞。
缓存击穿几种解决办法:
- 设置二级缓存,或者设置热点缓存永不过期,需要根据实际情况进行配置。
- 使用互斥锁,在执行过程中,如果缓存过期,那么先获取分布式锁,再执行从数据库中加载数据。如果找到数据就存入缓存,没有就继续该有的动作,在这个过程中能保证只有一个线程操作数据库,避免了对数据库的大量请求。
3、缓存雪崩

缓存雪崩: 当缓存服务器重启、或者大量缓存集中在某一个时间段失效,这样在失效的时候,也会给后端系统(比如DB)带来很大压力,造成数据库后端故障,从而引起应用服务器雪崩。
缓存雪崩几种解决办法:
- 缓存组件设计高可用,缓存高可用是指,存储缓存的组件的高可用,能够防止单点故障、机器故障、机房宕机等一系列问题。例如 Redis sentinel 和 Redis Cluster,都实现了高可用。
- 请求限流与服务熔断降级机制,限制服务请求次数,当服务不可用时快速熔断降级。
- 设置缓存过期时间一定的随机分布,避免集中在同一时间缓存失效。
- 定时更新缓存策略,对于实时性要求不高的数据,定时进行更新。
4、缓存一致性
使用缓存很大可能导致数据不一致问题,如下:
- 更熟数据库成功 -> 更新缓存失败 -> 数据不一致
- 更新缓存成功 -> 更新数据库失败 -> 数据不一致
- 更新数据库成功 -> 淘汰缓存失败 -> 数据不一致
- 淘汰缓存成功 -> 更新数据库失败 -> 查询缓存mis
所以使用缓存时候,应该结合实际情况,考虑缓存的数据是否有一致性需求。
四、SpringBoot 如何结合 Redis 实现缓存
1、Mavne 引入相关依赖
- spring-boot-starter-data-redis:
- commons-pool2:
1<dependency>
2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
4</dependency>
5<dependency>
6 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
7 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
8</dependency>
9<dependency>
10 <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
11 <artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
12</dependency>
2、配置 Redis 参数
application 文件中添加连接 Redis 的配置参数
- Redis 单机配置:
1spring:
2 redis:
3 host: 127.0.0.1 #Redis 地址
4 port: 6379 #Redis 端口号
5 database: 0 #Redis 索引(0~15,默认为0)
6 timeout: 1000 #Redis 连接的超时时间
7 password: 123456 #Redis 密码,如果没有就默认不配置此参数
8 lettuce: #使用 lettuce 连接池
9 pool:
10 max-active: 20 #连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
11 max-wait: -1 #连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
12 min-idle: 0 #连接池中的最大空闲连接
13 max-idle: 10 #连接池中的最小空闲连接
- Redis 哨兵配置:
1spring:
2 redis:
3 sentinel: #哨兵配置
4 master: "my-master"
5 nodes: "192.168.2.11:6379,192.168.2.12:6379,192.168.2.13:6379"
6 database: 0 #Redis 索引(0~15,默认为0)
7 timeout: 1000 #Redis 连接的超时时间
8 password: 123456 #Redis 密码,如果没有就默认不配置此参数
9 lettuce: #使用 lettuce 连接池
10 pool:
11 max-active: 20 #连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
12 max-wait: -1 #连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
13 min-idle: 0 #连接池中的最大空闲连接
14 max-idle: 10 #连接池中的最小空闲连接
15
- Redis 集群配置:
1spring:
2 redis:
3 cluster: #redis 集群配置
4 max-redirects: 5 #redis命令执行时最多转发次数
5 nodes: "192.168.2.11:6379,192.168.2.12:6379,192.168.2.13:6379"
6 database: 0 #Redis 索引(0~15,默认为0)
7 timeout: 1000 #Redis 连接的超时时间
8 password: 123456 #Redis 密码,如果没有就默认不配置此参数
9 lettuce: #使用 lettuce 连接池
10 pool:
11 max-active: 20 #连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
12 max-wait: -1 #连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
13 min-idle: 0 #连接池中的最大空闲连接
14 max-idle: 10 #连接池中的最小空闲连接
3、配置 Spring 缓存管理器
1@Configuration
2public class RedisConfig {
3
4 /**
5 * 配置缓存管理器
6 * @param factory Redis 线程安全连接工厂
7 * @return 缓存管理器
8 */
9 @Bean
10 public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
11 // 生成两套默认配置,通过 Config 对象即可对缓存进行自定义配置
12 RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfig = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
13 // 设置过期时间 10 分钟
14 .entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(10))
15 // 设置缓存前缀
16 .prefixKeysWith("cache:user:")
17 // 禁止缓存 null 值
18 .disableCachingNullValues()
19 // 设置 key 序列化
20 .serializeKeysWith(keyPair())
21 // 设置 value 序列化
22 .serializeValuesWith(valuePair());
23 // 返回 Redis 缓存管理器
24 return RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
25 .withCacheConfiguration("user", cacheConfig).build();
26 }
27
28 /**
29 * 配置键序列化
30 * @return StringRedisSerializer
31 */
32 private RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair<String> keyPair() {
33 return RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
34 }
35
36 /**
37 * 配置值序列化,使用 GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer 替换默认序列化
38 * @return GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer
39 */
40 private RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair<Object> valuePair() {
41 return RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
42 }
43
44}
4、服务中使用 SpringCache 的注解
1@Service
2@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "user")
3public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
4
5 /**
6 * 新增用户
7 */
8 public User addUser(User user) {
9 ......
10 }
11
12 /**
13 * 查询用户
14 */
15 @Cacheable(key = "#username")
16 public User getUserByUsername(String username) {
17 ......
18 }
19
20 /**
21 * 更新用户
22 */
23 @CachePut(key = "#user.username")
24 public User updateUser(User user) {
25 ......
26 }
27
28 /**
29 * 删除用户
30 */
31 @CacheEvict(key = "#username")
32 public void deleteByUsername(String username) {
33 ......
34 }
35
36}
注解说明:
- @CacheConfig: 一般配置在类上,指定缓存名称,这个名称是和上面“置缓存管理器”中缓存名称的一致。
- @Cacheable: 作用于方法上,用于对于方法返回结果进行缓存,如果已经存在该缓存,则直接从缓存中获取,缓存的key可以从入参中指定,缓存的 value 为方法返回值。
- @CachePut: 作用于方法上,无论是否存在该缓存,每次都会重新添加缓存,缓存的key可以从入参中指定,缓存的value为方法返回值,常用作于更新。
- @CacheEvict: 作用于方法上,用于清除缓存
- @Caching: 作用于方法上,用于一次性设置多个缓存。
上面注解中的常用配置参数:
- value: 缓存管理器中配置的缓存的名称,这里可以理解为一个组的概念,缓存管理器中可以有多套缓存配置,每套都有一个名称,类似于组名,这个可以配置这个值,选择使用哪个缓存的名称,配置后就会应用那个缓存名称对应的配置。
- key: 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合。
- condition: 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存。
- unless: 不缓存的条件,和 condition 一样,也是 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,为 true 时则不进行缓存。
5、启动类添加开启缓存注解
1@EnableCaching
2@SpringBootApplication
3public class Application {
4
5 public static void main(String[] args) {
6 SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
7 }
8
9}
- @EnableCaching: 作用于类上,用于开启注解功能。
五、SpringCache 操作缓存的不足
使用 Spring Cache 虽然方便,但是也有很多局限性,因为它多是根据请求参数命名 key,根据返回指设置 value,这样很多情况下,我们想方法内部进行命名和操作有一定的限制。如果我们需要灵活设置缓存,可以不用 SpringCache 提供的注解,直接在代码中使用 Spring-data-redis 包提供的方法,手动操作 key 与 value。
- opsForValue().set(String key, String value);
- opsForValue().get(String key);
1@Autowired
2private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
3
4public void redisBatch(){
5 // 设置值
6 redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key", "value");
7
8 // 获取值
9 redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("key");
10}
还有经常要批量设置、读取缓存,可以使用:
- opsForValue().multiSet(Map map);
- opsForValue().multiGet(List list);
1@Autowired
2private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
3
4public void redisBatch(){
5 // 批量设置值
6 Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
7 map.put("test1","value1");
8 map.put("test2","value2");
9 map.put("test3","value3");
10 redisTemplate.opsForValue().multiSet(map);
11
12 // 批量获取值,如果某个 key 不存在,则返回值集合中对于的为 null
13 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
14 list.add("test1");
15 list.add("test2");
16 list.add("test3");
17 List<Object> valueList = redisTemplate.opsForValue().multiGet(list);
18}
六、SpringBoot + SpringCache + Redis 示例项目
下面是一个简单的 SpringBoot 项目,用于对用户的增删改查,这里使用 SpringCache 来模拟对数据进行缓存,示例如下:
1、Mavne 引入相关依赖
Maven 中引入 SpringBoot 和 Redis 依赖,因为使用了
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
3 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
4 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
5
6 <parent>
7 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
8 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
9 <version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
10 </parent>
11
12 <groupId>mydlq.club</groupId>
13 <artifactId>springboot-redis-example</artifactId>
14 <version>0.0.1</version>
15 <name>springboot-redis-example</name>
16 <description>Demo project for Spring Boot Redis</description>
17
18 <properties>
19 <java.version>1.8</java.version>
20 </properties>
21
22 <dependencies>
23 <dependency>
24 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
25 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
26 </dependency>
27 <dependency>
28 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
29 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
30 </dependency>
31 <dependency>
32 <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
33 <artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
34 </dependency>
35 <dependency>
36 <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
37 <artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
38 </dependency>
39 </dependencies>
40
41 <build>
42 <plugins>
43 <plugin>
44 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
45 <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
46 </plugin>
47 </plugins>
48 </build>
49
50</project>
2、配置连接 Redis 参数
1spring:
2 redis:
3 host: 127.0.0.1
4 port: 6379
5 database: 0
6 timeout: 1000
7 password:
8 lettuce:
9 pool:
10 max-active: 20
11 max-wait: -1
12 min-idle: 0
13 max-idle: 10
3、配置 Spring 缓存管理器
缓存配置类,里面配置缓存管理器,配置缓存的全局过期时间、序列化等参数。
1import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
2import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
3import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
4import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
5import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
6import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
7import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.*;
8import java.time.Duration;
9
10/**
11 * Redis 配置类
12 */
13@Configuration
14public class RedisConfig {
15
16 /**
17 * 配置缓存管理器
18 * @param factory Redis 线程安全连接工厂
19 * @return 缓存管理器
20 */
21 @Bean
22 public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
23 // 生成两套默认配置,通过 Config 对象即可对缓存进行自定义配置
24 RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfig1 = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
25 // 设置过期时间 10 分钟
26 .entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(10))
27 // 设置缓存前缀
28 .prefixKeysWith("cache:user:")
29 // 禁止缓存 null 值
30 .disableCachingNullValues()
31 // 设置 key 序列化
32 .serializeKeysWith(keyPair())
33 // 设置 value 序列化
34 .serializeValuesWith(valuePair());
35 RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfig2 = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
36 // 设置过期时间 30 秒
37 .entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(30))
38 .prefixKeysWith("cache:user_info:")
39 .disableCachingNullValues()
40 .serializeKeysWith(keyPair())
41 .serializeValuesWith(valuePair());
42 // 返回 Redis 缓存管理器
43 return RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
44 .withCacheConfiguration("user", cacheConfig1)
45 .withCacheConfiguration("userInfo", cacheConfig2)
46 .build();
47 }
48
49 /**
50 * 配置键序列化
51 * @return StringRedisSerializer
52 */
53 private RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair<String> keyPair() {
54 return RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
55 }
56
57 /**
58 * 配置值序列化,使用 GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer 替换默认序列化
59 * @return GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer
60 */
61 private RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair<Object> valuePair() {
62 return RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
63 }
64
65}
4、定义实体类
用户实体类
User
1import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
2import lombok.Data;
3
4/**
5 * 用户实体
6 */
7@Data
8public class User {
9 private String username;
10 @JsonProperty(access = JsonProperty.Access.WRITE_ONLY)
11 private String password;
12 private String role;
13}
用户信息实体类
UserInfo
1import lombok.Data;
2
3/**
4 * 用户信息实体
5 */
6@Data
7public class UserInfo {
8 private String name;
9 private String sex;
10 private Integer age;
11}
5、定义服务接口
UserService
1import mydlq.club.example.entity.User;
2
3/**
4 * 用户业务接口
5 */
6public interface UserService {
7
8 /**
9 * 增加账户
10 *
11 * @param user 账户
12 */
13 void addUser(User user);
14
15 /**
16 * 获取账户
17 *
18 * @param username 用户名
19 * @return 用户信息
20 */
21 User getUserByUsername(String username);
22
23 /**
24 * 修改账户
25 *
26 * @param user 用户信息
27 * @return 用户信息
28 */
29 User updateUser(User user);
30
31 /**
32 * 删除账户
33 * @param username 用户名
34 */
35 void deleteByUsername(String username);
36
37}
UserInfoService
1import mydlq.club.example.entity.UserInfo;
2
3/**
4 * 用户信息业务接口
5 */
6public interface UserInfoService {
7
8 /**
9 * 增加用户信息
10 *
11 * @param userInfo 用户信息
12 */
13 void addUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo);
14
15 /**
16 * 获取用户信息
17 *
18 * @param name 姓名
19 * @return 用户信息
20 */
21 UserInfo getByName(String name);
22
23 /**
24 * 修改用户信息
25 *
26 * @param userInfo 用户信息
27 * @return 用户信息
28 */
29 UserInfo updateUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo);
30
31 /**
32 * 删除用户信息
33 * @param name 姓名
34 */
35 void deleteByName(String name);
36
37}
6、实现服务类
实现 UserService 与 UserInfoService 接口中的方法,里面使用 @Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict 三个注解完成对用户与用户信息数据的缓存。
UserServiceImpl(用户业务实现类)
注意,为了演示方便,没有连接数据库,临时创建了个成员变量 userMap 来模拟数据库存储。
1import mydlq.club.example.entity.User;
2import mydlq.club.example.service.UserService;
3import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
4import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
5import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
6import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
7import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
8import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
9import java.util.HashMap;
10
11@Service
12@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "user")
13public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
14
15 private HashMap<String, User> userMap = new HashMap<>();
16
17 @Override
18 public void addUser(User user) {
19 userMap.put(user.getUsername(), user);
20 }
21
22 @Override
23 @Cacheable(key = "#username",unless = "#result==null ")
24 public User getUserByUsername(String username) {
25 if (!userMap.containsKey(username)) {
26 return null;
27 }
28 return userMap.get(username);
29 }
30
31 @Override
32 @CachePut(key = "#user.username")
33 public User updateUser(User user) {
34 if (!userMap.containsKey(user.getUsername())){
35 throw new RuntimeException("不存在该用户");
36 }
37 // 获取存储的对象
38 User newUser = userMap.get(user.getUsername());
39 // 复制要更新的数据到新对象,因为不能更改用户名信息,所以忽略
40 BeanUtils.copyProperties(user, newUser, "username");
41 // 将新的对象存储,更新旧对象信息
42 userMap.put(newUser.getUsername(), newUser);
43 // 返回新对象信息
44 return newUser;
45 }
46
47 @Override
48 @CacheEvict(key = "#username")
49 public void deleteByUsername(String username) {
50 userMap.remove(username);
51 }
52
53}
UserInfoServiceImpl(用户信息业务实现)
注意,为了演示方便,没有连接数据库,临时创建了个成员变量 userInfoMap 来模拟数据库存储。
1import mydlq.club.example.entity.UserInfo;
2import mydlq.club.example.service.UserInfoService;
3import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
4import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
5import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
6import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
7import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
8import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
9import java.util.HashMap;
10
11@Service
12@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "userInfo")
13public class UserInfoServiceImpl implements UserInfoService {
14
15 private HashMap<String, UserInfo> userInfoMap = new HashMap<>();
16
17 @Override
18 public void addUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo) {
19 userInfoMap.put(userInfo.getName(), userInfo);
20 }
21
22 @Override
23 @Cacheable(key = "#name", unless = "#result==null")
24 public UserInfo getByName(String name) {
25 if (!userInfoMap.containsKey(name)) {
26 return null;
27 }
28 return userInfoMap.get(name);
29 }
30
31 @Override
32 @CachePut(key = "#userInfo.name")
33 public UserInfo updateUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo) {
34 if (!userInfoMap.containsKey(userInfo.getName())) {
35 throw new RuntimeException("该用户信息没有找到");
36 }
37 // 获取存储的对象
38 UserInfo newUserInfo = userInfoMap.get(userInfo.getName());
39 // 复制要更新的数据到新对象,因为不能更改用户名信息,所以忽略
40 BeanUtils.copyProperties(userInfo, newUserInfo, "name");
41 // 将新的对象存储,更新旧对象信息
42 userInfoMap.put(newUserInfo.getName(), newUserInfo);
43 // 返回新对象信息
44 return newUserInfo;
45 }
46
47 @Override
48 @CacheEvict(key = "#name")
49 public void deleteByName(String name) {
50 userInfoMap.remove(name);
51 }
52
53}
7、创建 Controller
UserController
1import mydlq.club.example.entity.User;
2import mydlq.club.example.service.UserService;
3import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
4import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
5
6/**
7 * 用户 Controller
8 */
9@RestController
10public class UserController {
11
12 @Autowired
13 private UserService userService;
14
15 @GetMapping("/user/{username}")
16 public User getUser(@PathVariable String username) {
17 return userService.getUserByUsername(username);
18 }
19
20 @PostMapping("/user")
21 public String createUser(@RequestBody User user) {
22 userService.addUser(user);
23 return "SUCCESS";
24 }
25
26 @PutMapping("/user")
27 public User updateUser(@RequestBody User user) {
28 return userService.updateUser(user);
29 }
30
31 @DeleteMapping("/user/{username}")
32 public String deleteUser(@PathVariable String username) {
33 userService.deleteByUsername(username);
34 return "SUCCESS";
35 }
36
37}
UserInfoController
1import mydlq.club.example.entity.UserInfo;
2import mydlq.club.example.service.UserInfoService;
3import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
4import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
5
6/**
7 * 用户信息 Controller
8 */
9@RestController
10public class UserInfoController {
11
12 @Autowired
13 private UserInfoService userInfoService;
14
15 @GetMapping("/userInfo/{name}")
16 public UserInfo getUserInfo(@PathVariable String name) {
17 return userInfoService.getByName(name);
18 }
19
20 @PostMapping("/userInfo")
21 public String createUserInfo(@RequestBody UserInfo userInfo) {
22 userInfoService.addUserInfo(userInfo);
23 return "SUCCESS";
24 }
25
26 @PutMapping("/userInfo")
27 public UserInfo updateUserInfo(@RequestBody UserInfo userInfo) {
28 return userInfoService.updateUserInfo(userInfo);
29 }
30
31 @DeleteMapping("/userInfo/{name}")
32 public String deleteUserInfo(@PathVariable String name) {
33 userInfoService.deleteByName(name);
34 return "SUCCESS";
35 }
36
37}
8、启动类
启动类中添加 @EnableCaching 注解开启缓存。
1import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
2import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
3
4@EnableCaching
5@SpringBootApplication
6public class Application {
7
8 public static void main(String[] args) {
9 SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
10 }
11
12}
---END---

!版权声明:本博客内容均为原创,每篇博文作为知识积累,写博不易,转载请注明出处。